Hamstring Strains: Causes, Symptoms, and Evidence-Based Treatments
Hamstring strains are a common musculoskeletal injury, particularly among athletes and individuals engaged in physical activities.
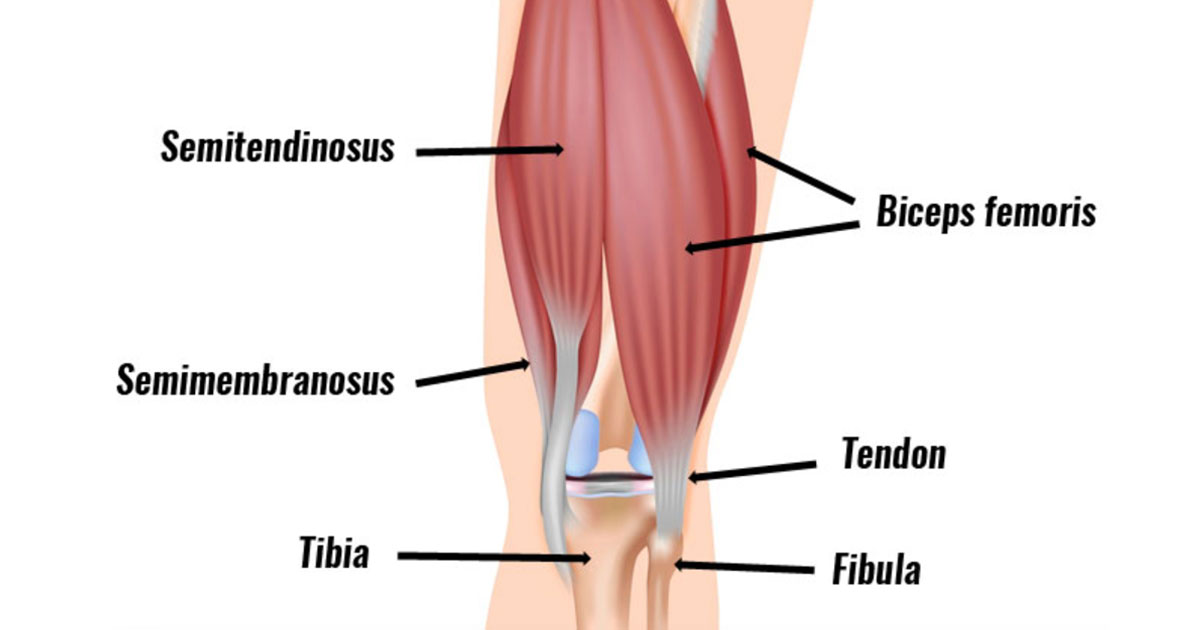
What are the hamstrings?
The hamstrings are a group of three muscles located on the back of the thigh: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus.
These muscles play a crucial role in knee flexion and hip extension, making them essential for various movements such as running, jumping, and kicking. When these muscles are subjected to excessive force or stretched beyond their limits, it can result in a hamstring strain.
What are the causes of hamstring strains?
Hamstring strains often occur during activities that involve sudden acceleration or deceleration, such as sprinting, jumping, or rapid changes in direction. Some common causes include:
1. Muscle Imbalance: Weakness or imbalance between the hamstring and quadriceps muscles can increase the risk of hamstring strains.
2. Poor Flexibility: Inadequate flexibility in the hamstrings and surrounding muscles can lead to increased susceptibility to injury.
3. Fatigue: Muscular fatigue, especially in athletes participating in prolonged or intense training sessions, can compromise muscle function and increase the risk of strain.
4. Overuse: Repeated stress on the hamstring muscles without adequate rest and recovery can result in overuse injuries, including strains.
What are the symptoms of hamstring strains?
Hamstring strains can vary in severity, but common symptoms include:
1. Pain: A sudden, sharp pain in the back of the thigh during physical activity.
2. Tenderness: Tenderness and swelling in the affected area.
3. Bruising: Bruising or discoloration may develop along the back of the thigh.
4. Weakness: Difficulty with activities such as walking, running, or bending the knee.
5. Stiffness: Limited range of motion and stiffness in the hamstring muscles.
What is the treatment for hamstring strains?
The treatment of hamstring strains typically involves a combination of conservative measures aimed at reducing pain, inflammation, and promoting healing. Evidence-based treatments include:
1. Rest and Activity Modification: Resting the injured leg and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain or discomfort is crucial in the acute phase of injury. Gradual reintroduction of activity is recommended once pain and swelling subside, guided by a healthcare professional.
2. Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the injured area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Ice therapy is most effective when applied for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the initial 48-72 hours following injury.
3. Compression and Elevation: Compression bandages can help reduce swelling, while elevating the leg above heart level can aid in fluid drainage and minimize swelling.
4. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen may be recommended to alleviate pain and inflammation for a short period. They should not be used with in the first 72 hours, so as not to inhibit the body’s initial inflammatory response.
5. Physiotherapy: A structured physiotherapy program is essential for rehabilitation and preventing recurrent injuries. Therapeutic exercises focus on improving flexibility, strength, and neuromuscular control of the hamstring muscles. Building a progressive strengthening programme is essential, to promote tissue healing and decrease the risk of reinjury.
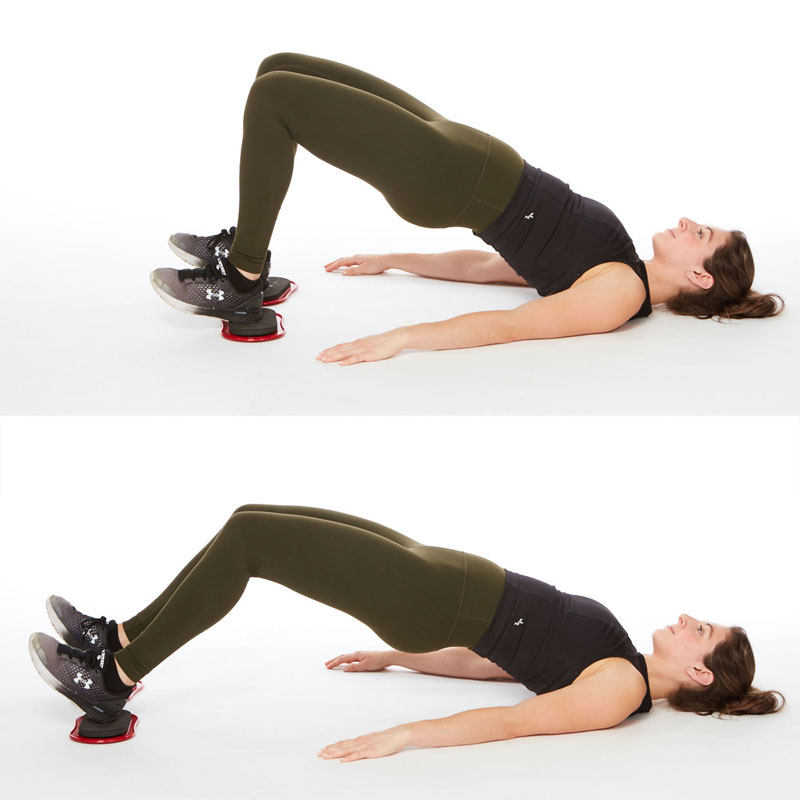

Hamstring slides – late stage rehab
6. Return to Activity: Gradual return to sport or physical activity is crucial to prevent reinjury. Athletes should meet specific criteria, including pain-free range of motion, adequate strength and flexibility, and sport-specific functional testing before returning to full activity.
Hamstring strains are a common and often debilitating injury, particularly among athletes. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and evidence-based treatments is essential for effective management and rehabilitation. While most hamstring strains can be successfully treated with conservative measures, severe or recurrent injuries may require surgical intervention. Early recognition, appropriate treatment, and comprehensive rehabilitation are key to minimizing downtime and preventing long-term complications associated with hamstring strains.

